News
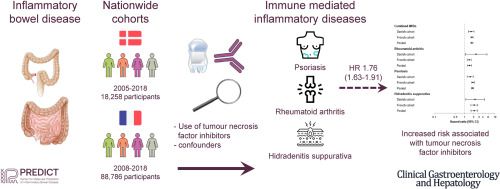
Anti-TNF therapy for IBD patients is associated with increased risk to Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases
Anti-TNFs are primary therapies for several immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs). However, case studies have revealed the paradoxical occurrence of IMIDs in patients treated with anti-TNF. The authors in this study conducted 2 nationwide cohort studies comprising all patients with IBD in Denmark (2005–2018) and France (2008–2018). They showed that anti-TNF was associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and hidradenitis suppurativa in both the Danish and the French cohort. Anti-TNF was also associated with an increased risk of the outcomes when compared with azathioprine suggesting that anti-TNF therapy was associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.